Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is not just about keywords and content. Behind the scenes, technical SEO plays a massive role in determining how search engines crawl, understand, and rank your website. One of the most important—but often misunderstood—technical SEO files is robots.txt.
If you’re asking what is robots.txt in SEO, this guide will give you a complete, easy-to-understand explanation. We’ll cover what robots.txt is, how it works, why it matters, best practices, common mistakes, and how to optimize it for better SEO performance.
What Is Robots.txt in SEO?
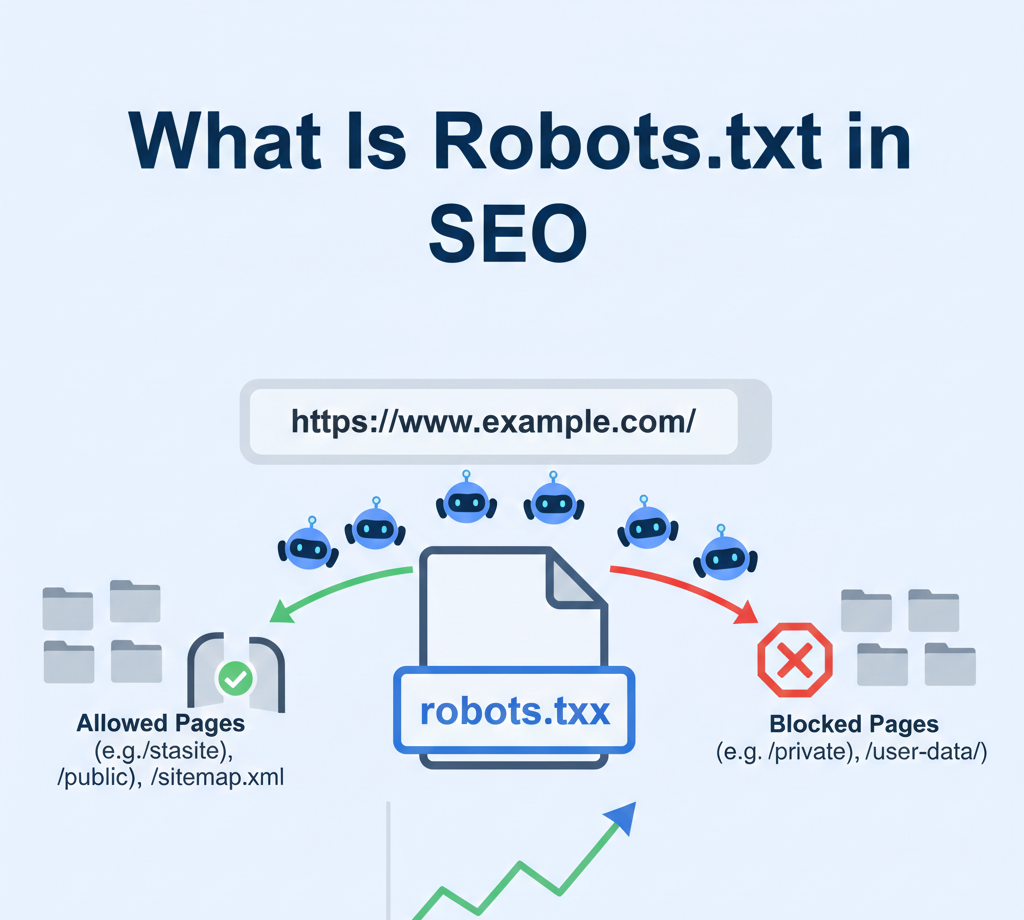
Robots.txt is a simple text file placed in the root directory of a website that tells search engine crawlers which pages or sections of a site they are allowed or not allowed to crawl.
In SEO, robots.txt is used to control search engine crawling behavior, helping search engines focus on important pages while avoiding unnecessary or sensitive areas.
In simple terms:
👉 Robots.txt acts like a traffic controller for search engine bots.
Example of a robots.txt file location:
https://www.example.com/robots.txt
Why Robots.txt Is Important for SEO
Understanding what is robots.txt in SEO is critical because this file directly impacts how search engines interact with your website.
Key SEO Benefits of Robots.txt
- Controls crawl budget usage
- Prevents crawling of duplicate or low-value pages
- Protects sensitive or private sections
- Improves website performance
- Helps search engines prioritize important content
When used correctly, robots.txt improves crawling efficiency and strengthens your overall SEO strategy.
How Robots.txt Works
Search engine bots like Googlebot, Bingbot, and others look for the robots.txt file before crawling any website. If they find it, they read and follow the instructions written inside.
The file uses simple rules, including:
- User-agent – Specifies which bot the rule applies to
- Disallow – Tells bots not to crawl a specific path
- Allow – Permits crawling of specific files or folders
Basic Robots.txt Example
User-agent: *
Disallow: /admin/
This means:
All search engine bots are not allowed to crawl the /admin/ directory.
Robots.txt vs Meta Robots Tag (Important Difference)
Many people confuse robots.txt with meta robots tags, but they serve different purposes.
| Feature | Robots.txt | Meta Robots Tag |
|---|---|---|
| Controls crawling | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Controls indexing | ❌ No (indirect) | ✅ Yes |
| Page-level control | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Site-wide control | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
👉 Robots.txt controls crawling, not indexing.
A blocked page may still appear in search results if it’s linked elsewhere.
Common Directives Used in Robots.txt

To fully understand what is robots.txt in SEO, you must know its directives.
1. User-agent
Specifies which crawler the rule applies to.
User-agent: Googlebot
2. Disallow
Blocks crawling of a specific page or directory.
Disallow: /private/
3. Allow
Allows crawling of specific files within a blocked directory.
Allow: /images/logo.png
4. Sitemap (SEO Best Practice)
Helps search engines find your sitemap easily.
Sitemap: https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml
Why Crawl Budget Matters in SEO
Crawl budget is the number of pages a search engine is willing to crawl on your website within a given time.
Robots.txt helps optimize crawl budget by:
- Blocking unnecessary URLs (filters, parameters)
- Preventing crawling of duplicate pages
- Allowing faster discovery of important content
This is especially important for large websites, eCommerce stores, and news portals.
What Should You Block Using Robots.txt?
Here are common sections that are usually safe to block:
- Admin panels
- Login and signup pages
- Internal search result pages
- Shopping cart and checkout pages
- Filtered URLs with parameters
Example:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /wp-admin/
Disallow: /cart/
Disallow: /checkout/
What You Should NOT Block in Robots.txt
Blocking the wrong pages can seriously harm your SEO.
❌ Do not block:
- CSS and JavaScript files (Google needs them)
- Important landing pages
- Blog posts or product pages
- Pages you want indexed
Blocking resources can break page rendering and reduce rankings.
Robots.txt and Google SEO Guidelines
Google officially recommends:
- Allowing CSS and JS files
- Using robots.txt only for crawl control
- Using
noindexfor index control - Keeping robots.txt simple and clean
Incorrect robots.txt rules are one of the most common technical SEO mistakes.
Robots.txt for WordPress Websites
Most WordPress sites generate a default robots.txt file automatically.
A recommended WordPress robots.txt example:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /wp-admin/
Allow: /wp-admin/admin-ajax.php
Sitemap: https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml
This blocks admin areas but allows important AJAX functionality.
Robots.txt for eCommerce SEO

For eCommerce sites, robots.txt is crucial because of duplicate URLs caused by filters and sorting.
Common blocks include:
- Product filters
- Session IDs
- Sorting parameters
Example:
Disallow: /*?sort=
Disallow: /*?filter=
This helps search engines focus on core product and category pages.
How Robots.txt Affects Indexing
A common myth in SEO is that robots.txt prevents indexing.
❗ Important truth:
Robots.txt does not guarantee deindexing.
If a blocked page has backlinks, Google may still index it without content. To prevent indexing, use:
noindexmeta tag- Password protection
- HTTP authentication
How to Test Robots.txt (Very Important)
Always test your robots.txt file to avoid SEO disasters.
Tools to Use:
- Google Search Console Robots.txt Tester
- URL Inspection Tool
- Manual browser testing
Testing ensures important pages are not accidentally blocked.
Common Robots.txt Mistakes to Avoid
Here are some costly mistakes:
- Blocking the entire website
Disallow: /
- Blocking CSS and JS files
- Using incorrect syntax
- Forgetting to update after site changes
- Blocking staging URLs incorrectly
One small error can remove your entire site from search visibility.
Best Practices for Robots.txt in SEO
To use robots.txt effectively, follow these best practices:
- Keep it simple and readable
- Block only what is necessary
- Always include your sitemap
- Test before publishing
- Review after site updates
- Combine with proper indexing strategies
A clean robots.txt file improves crawling efficiency and SEO performance.
Robots.txt and Website Security (Important Note)

Robots.txt is not a security tool.
Anyone can view your robots.txt file, so:
- Do not list sensitive directories
- Do not rely on it to protect private data
Use authentication or server-level security instead.
How Often Should You Update Robots.txt?
You should review robots.txt when:
- Launching a new website
- Migrating domains
- Redesigning site structure
- Adding eCommerce filters
- Fixing crawl issues
SEO is ongoing, and robots.txt should evolve with your site.
Future of Robots.txt in SEO
As search engines evolve, robots.txt remains relevant but more refined.
Future trends include:
- Smarter crawl prioritization
- AI-driven crawling behavior
- Stronger integration with technical SEO audits
- Increased importance for large sites
Understanding what is robots.txt in SEO will remain a core technical SEO skill.
Final Thoughts: What Is Robots.txt in SEO?
Robots.txt is a powerful yet simple file that plays a crucial role in SEO. It helps search engines crawl your website efficiently, conserve crawl budget, and focus on your most valuable pages.
When used correctly, robots.txt supports better rankings, faster indexing, and stronger technical SEO health. When misused, it can block visibility and damage performance.
If you want a solid SEO foundation, mastering robots.txt is not optional—it’s essential.